
Fungal scalp is a problem that oftenoccurs in modern dermatology. And although the first stages of the development of the disease can proceed without any visible symptoms and do not bring a person discomfort, treatment is necessary here. In the absence of therapy, fungal infections can lead to partial or complete alopecia.
Where does the fungus of the scalp come from?
Dozens of modern medicine are knownvarieties of fungal skin lesions. Each disease is accompanied by different symptoms. As for the pathogens themselves, there is a very large group of pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms capable of affecting the scalp.
Transmission paths can also be different. But in most cases, you can catch an infection during close contact with a sick person. Sometimes there is also a domestic infection when sharing hygiene items, towels, combs, bed linens, etc.
Of course, the development of the disease can lead tooutbreak of opportunistic fungi - saprophytes. Such microorganisms are "permanent residents" of human skin, but their numbers are strictly regulated by the immune system. Therefore, the fungus of the scalp is often observed against the background of a decrease in the body's defenses. Risk factors also include diseases of the endocrine system and malfunctions of the hormonal background.
The most common lesions of the scalp include seborrhea, epidermophytosis, trichophytosis, colorful lichen and favus.
Fungal head skin: symptoms and signs of disease

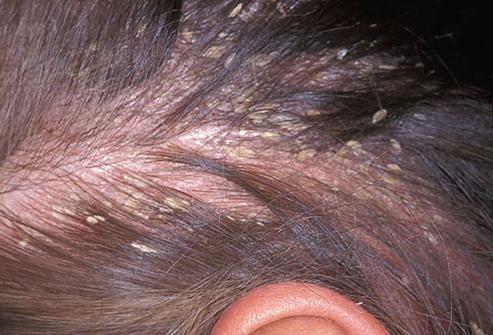
The clinical picture depends onA variety of infection and severity of the disease. Nevertheless, there are some common symptoms. Fungus of the scalp, usually accompanied by dry skin and severe itching. Most lesions have an oval shape.
The main symptoms includeredness, and sometimes swelling of the scalp. Since infected with fungi, it becomes dry, sensitive and covered with microcracks, often the disease is associated with secondary infection. In turn, with this complication, small pustules are often formed. As the disease progresses, the skin begins to peel off and is covered with crusts of white, yellowish or even brown color.
In most cases, the fungus affects not onlythe skin itself, but also the hair follicles. Against the background of infection, the head of hear noticeably thinens - the hair becomes brittle, dull and thin. For example, with microsporia, the hairs break off approximately 5-7 millimeters from the surface of the skin, and the remaining fibers become whitish in color.
How to treat a head skin fungus?

With a similar problem, it's best to contactto a dermatologist or trichologist. After all, only a specialist knows how the fungus of the scalp looks, symptoms, treatment of the disease. But self-medication is not worth it. Do not forget that in the absence of proper therapy, the infection can spread to deeper layers of the skin, and sometimes even to nails and mucous membranes.
Fortunately, modern medicine has a massreally effective antifungal medicines. Typically, for this purpose, special shampoos, gels or hair masks that contain ketoconazole and other active substances are used. In particular, shampoo "Nizoral" is considered quite effective today. In more severe cases, systemic treatment is required - patients are prescribed the use of such drugs as "Fluconazole", "Levorin" and "Terbinafine."
You can use some methods of the people'smedicine. For example, in the water for washing your head, you can add a few drops of tea tree oil, jojoba or eucalyptus, since they have antiseptic properties, both moisturize and soothe the skin.
